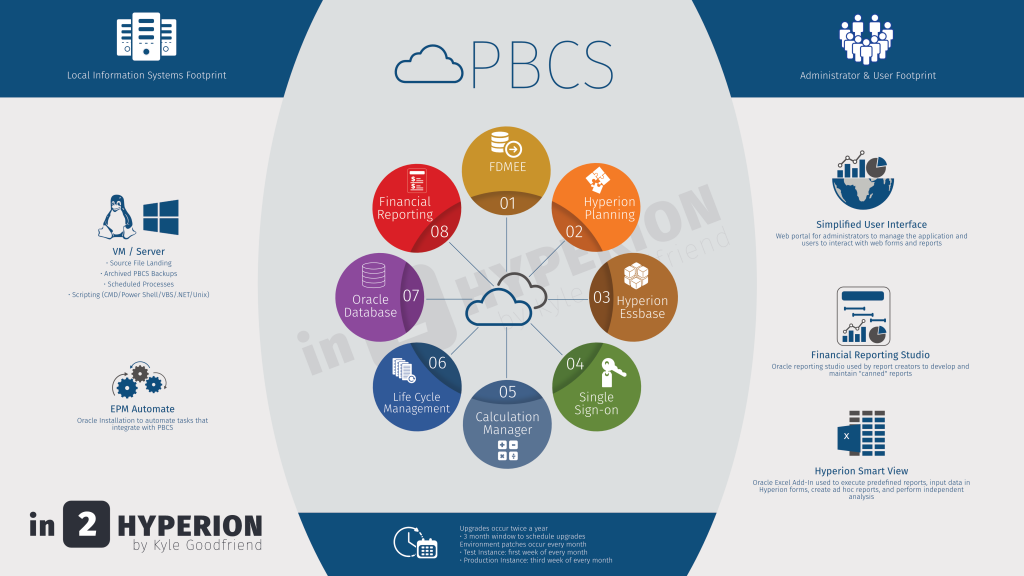
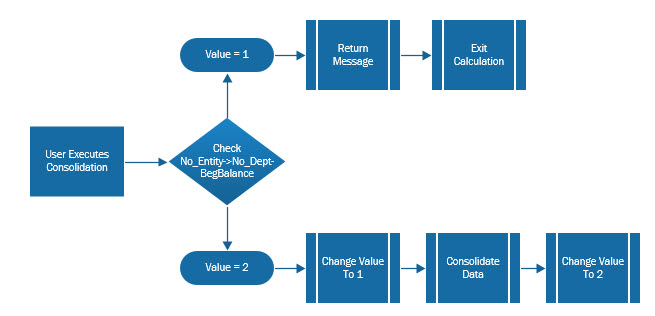
Use PowerShell to split large files by month/year for data loads into FDMEE on PBCS
If you are using PBCS, you may run into some challenges with large files being passed through FDMEE. Whether performance is an issue or you just want to parse a file my month/year, this script might save you some time.
The Challenge
I recently had the need to break apart a file. The source provided one large text file that included 2 years of data that was needed to populate the history of an employee metrics application. The current process loaded files by month and we wanted to be able to piggy back off the existing scripts to load and process data in FDMEE and the monthly Planning data pushes to the ASO reporting cube. So, the need break the data file into seperate files by month and year was required. The file was delimited and formatted like the following.
Entity,Year,Scenario,Period,Account,Date,Employee,Pay Code,JobNumber,Data
BU1005,FY15,Actual,Feb,Pay Amount,02/02/2015,V1398950,P105,,108.10
BU1005,FY15,Actual,Feb,Pay Amount,02/03/2015,V1398950,P105,,108.92
The goal was to have a file for every unique month and year combination that included only the lines of the relevant time periods. The header of the file also had to exist in each of the smaller files. Since we were working on a Windows machine, we used PowerShell to script the solution.
Powershell Script Directions
The script is pretty simple to use and understand. Update the script as follows.
- Create a new text file with a ps1 extension and paste the following into that file.
- Update the srcFile variable to point to the file to be parsed.
- Update the startYear to the first year in the file to be extracted.
- Update the currentYear variable to the last year in the file to be extracted.
- Update the ProcessName to a meaningful word or phrase that will be used to create the file name.
- Save the file and execute it like any other PowerShell script.
This will produce 12 files for each year with the header line and the data related to the month and year that represents the year and month in the file name.
Disclaimer
I welcome feedback on improving performance and will give credit to anybody that can improve on this. I am NOT an expert in PowerShell and I am sure there are faster ways to accomplish this. This created 12 files (1 year / 12 months) from a file that includes 7.8 million records and completed in 24 minutes. So, this is pretty reasonable for one-off requests, but might need attention if it was a repeatable need.
This was developed using PowerShell 5 and some functions do not work in earlier adoptions of the software.
Powershell Script
####################################################################### # Set the file to parse # # Set the start year and end year # # Change the counter if you want the files produced to start at # something other than 1 #######################################################################
# Write a status to the screen to monitor progress write-host "Processing started at $($(Get-Date).ToShortTimeString())" # Update to point to the source file $srcFile = "C:\Oracle\GCA\Data\Files\2015 Time Data\Time_DataPayAmount2015.csv" # Set to the first year you want to process $startYear = 2015 # Set to the last year you want to process $currentYear = 2016 # Used in the naming, is the starting number in name and increments by 1 $counter = 1 # Get the first line (the header line) of the file $Header = Get-Content $srcFile -First 1 # Set the process name used in the file name $ProcessName = "Test Process" # Loop through each year in the range ForEach ($Years in $startYear..$currentYear ) { # Loop through each month of the year ForEach ($months in 1..12 ) { # Get the 3 month abbreviation of the month being processed $ShortMonth = (Get-Culture).DateTimeFormat.GetAbbreviatedMonthName($months) # Format year to FYxx (This is typically required on a Planning application) $FormattedYear = "FY" + $Years.ToString().substring($Years.ToString().length - 2, 2) # Set the file name to a number starting with 1, the Month, and the year # Example: 01_ProcessName_Jan_2015.txt $FileOut = "{0:00}" -f $counter++ + "_" + $ProcessName + "_" + $ShortMonth + "_" + $Years + '.txt' # Write out the header to the newly created file file $Header | out-file -filepath $FileOut -Encoding utf8 # Write out all the lines that match the month and year. The pattern # includes a ".*" which is the equivalent of an AND conjunction, so # the line has to include the processing year AND processing month # for it to be included. select-string $srcFile -pattern "${FormattedYear}.*($($ShortMonth))" | foreach {$_.Line} | out-file -filepath $FileOut -Encoding utf8 -Append # Write a status to the screen - this is not required but provides a level # of the current progress by communicating the Month/Year completed and the # time it completed write-host $fileout "Completed at $($(Get-Date).ToShortTimeString())" } }
Conclusion
Hopefully this will benefit the community. As I create more scripts like this, I plan to share them.
 Kscope wouldn’t be the same without checking out Jake – one of the best. The amount of time and effort he puts into his presentations is crazy and it shows. If you want to learn something new, below is schedule. If you get a picture of him in his formal wear (you will know what I mean if you see it), please post a picture in a comment and tweet me…PLEASE!
Kscope wouldn’t be the same without checking out Jake – one of the best. The amount of time and effort he puts into his presentations is crazy and it shows. If you want to learn something new, below is schedule. If you get a picture of him in his formal wear (you will know what I mean if you see it), please post a picture in a comment and tweet me…PLEASE!