Goodbye to the days of JavaScript in order to enforce data input policies and rules to Planning web forms. With Planning version 11.1.2 and newer, Oracle has introduced a powerful set of tools for data validation within the Planning Data Form Designer itself. Let’s walk through a scenario of how this works.
Say that we have a product mix form that will be used to input percentages as drivers for a revenue allocation. Here’s what the form looks like:
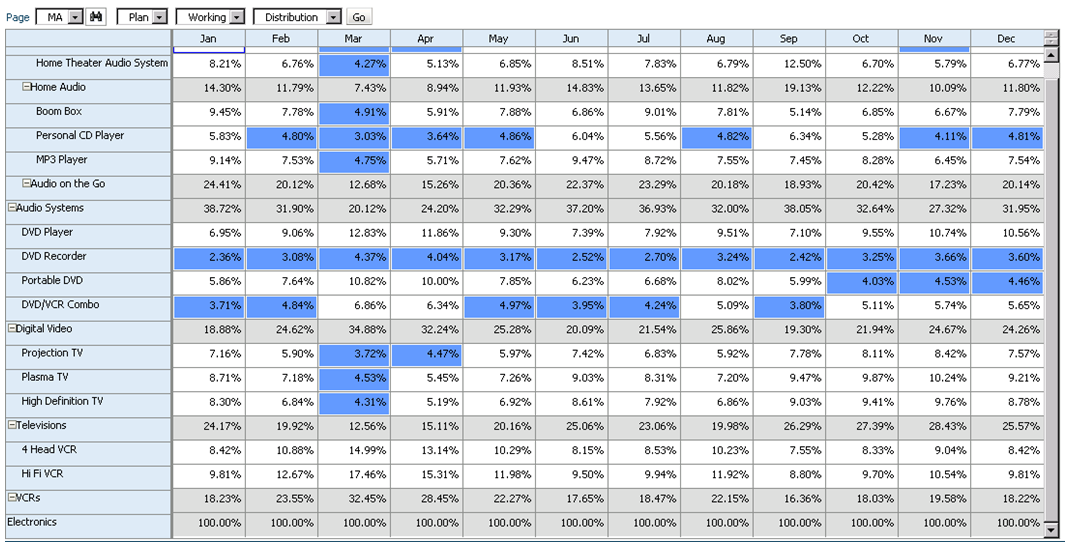
We should expect that the sum of these percentages to be 100% at the “Electronics” parent member. If this is not the case, the revenue allocation will incorrectly allocate data across products. So how do we enforce this rule? Simple… let’s take a look at the data form design.
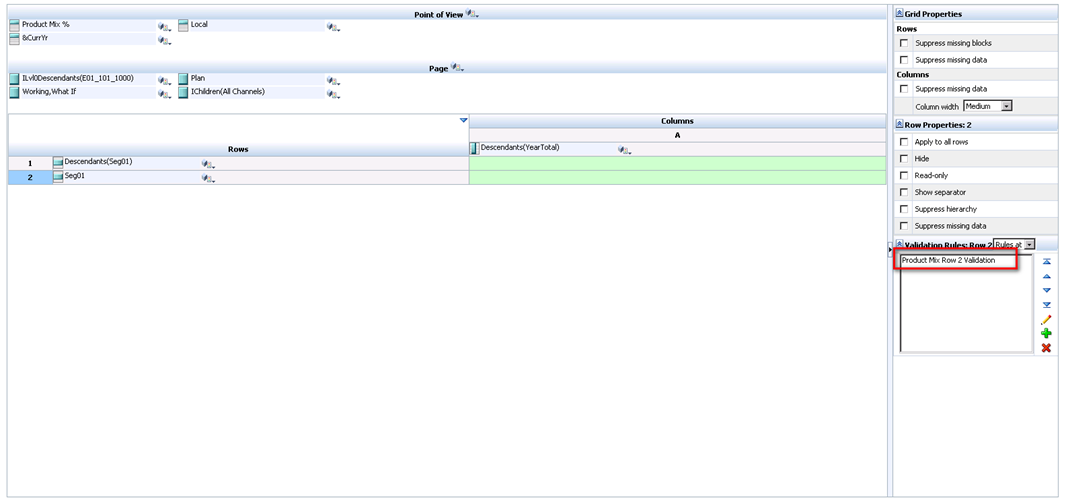
As a row definition we’ve included two member selections; 1) Descendants(Seg01) or Descendants(Electronics) and 2) Seg01 or Electronics. We are going to add a validation rule to row 2 of the data form. To do this, highlight row 2 and click the sign to add a new validation rule. Notice that in the validation rules section, it now says ‘Validation Rules: Row 2’.

The Data Validation Rule Builder will then be launched. Let’s fill in the rule. We should ensure the Location is set to ‘Row 2’. We’ve filled in a name and quick description, then ensured that the ‘Enable validation rule’ check box is checked.
For the rule we’ve defined some simple if logic:
IF [Current Cell Value] != [Value = 1] THEN [Process Cell] ;
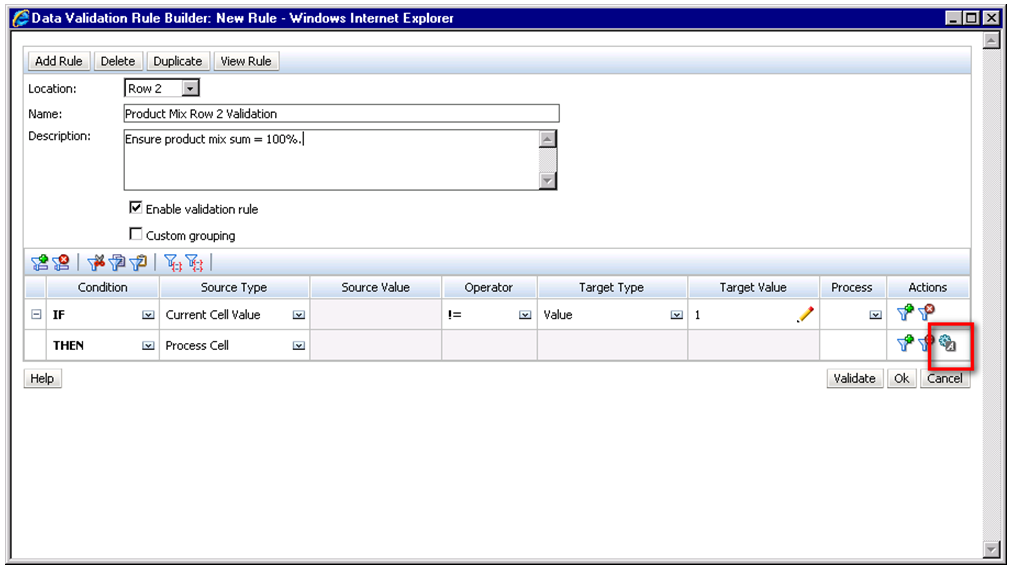
To define what occurs if this condition is met we choose the ‘Process Cell’ action defined by the small gear with a letter A next to it. Here we will highlight the cell red and notify the user with a validation message.

We click through to save the Process Cell definition and the Validation Rule itself and should now see the rule in the data form definition.
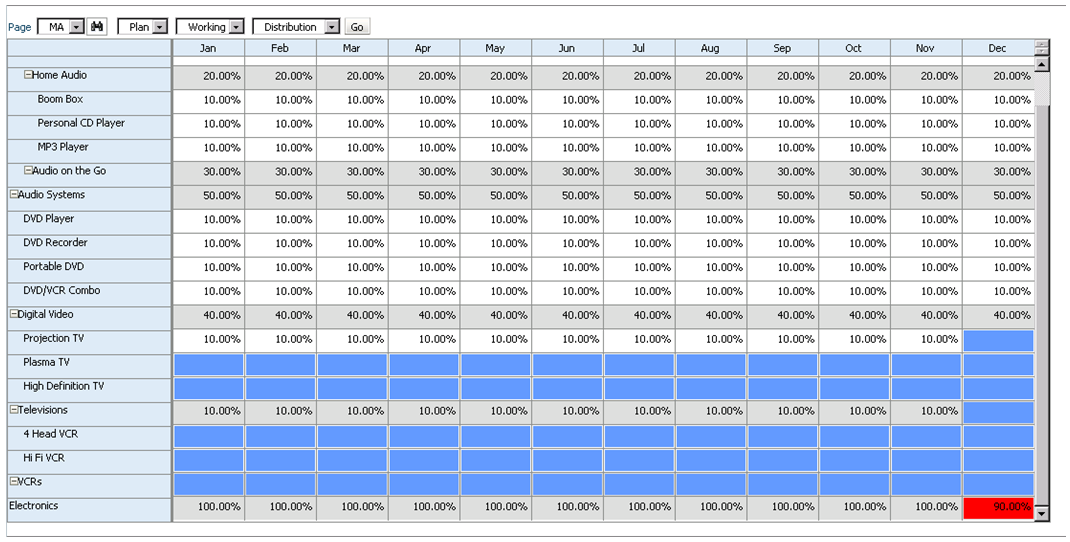
So let’s take a look at how the end user will interact with this form. Percentages are entered by product for each month. Upon save, notice that all months for Electronics that equal 100% appear normal. December only sums to 90% and is highlighted in red as we specified in the data validation rule. We cannot limit the user’s ability to save the form until the cell equals 100%; we can only notify them of the issue, and explain the cause and potential resolutions.
Of course, this is a simple example of what can be done using Planning’s Data Validation Rules. The possibilities are endless. Oracle has more scenario walkthroughs in the Planning Administrator’s Guide. View them here: http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E17236_01/epm.1112/hp_admin/ch08.html






