Adventures in Groovy – Part 2: Data Validation
Introduction
We all know the Data Form validation rules are serviceable, but they are not robust. When Smart View advanced and forms were opened in Excel, the validation logic developers had in JavaScript became useless. Since then, we have really missed the ability to communicate with the user interactively with visual cues and validation rules that halted the saving of data. Well, Groovy calculations to the rescue!
I will preface with the fact that I am encountering some odd behavior, so I am going to break this up into multiple articles. It appears that Oracle is validating Groovy enhancements in Data Forms on the web, and not necessarily testing the full functionality in Smart View. Currently, I have this working in a browser perfectly, but 3 of the 8 columns are failing in Smart View. I am hoping to get closure to a ticket on this in the near future. When I get a resolution, I will amend this article with some clarity on either what I am doing wrong, or when it will be resolved.
High Level requirement
At a high level, the planners want to see any seeded value that was changed with a different background color to single out the lines that have been edited.
The Details
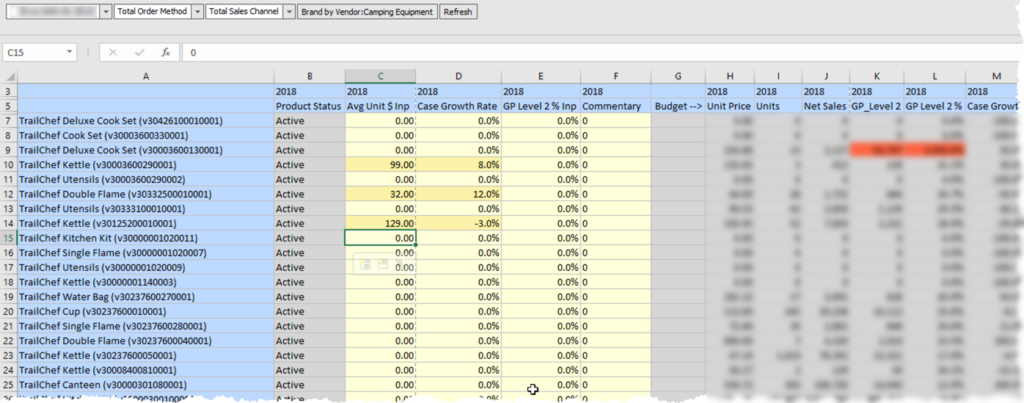
We have a form that provides the users the ability to override seeded data. In this example, a planner can change the Average Price/Case, Net Sales, and/or GP Level 2 at any level of the hierarchy and gets allocated down to level 0 on a % to Total. This form has the accounts in question for 3 sources. The override columns are a separate version that is set to top down so security doesn’t prevent them from entering at a non-level 0 member. This is only used to enter the 3 values, is used to calculate the Input source, and is cleared.

The Initialized source is seeded from prior year growth. This, in essence, is the basline seeded amount. At initialization, the Input source is a duplicate of Initialized source.

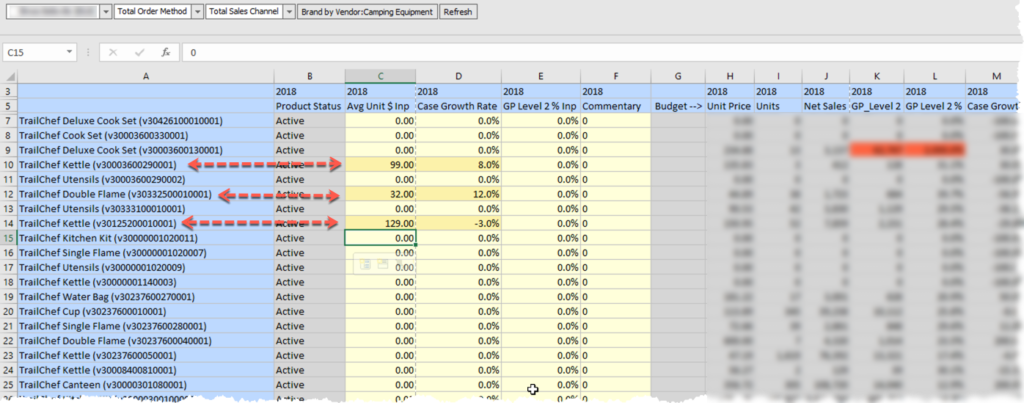
The Initialized source is also on the form. When overrides are entered, it is applied to the input source. At this point in the process, the Input is different from the Initialized source, as shown by the orange color in the previous image.

Why Not Validation Rules?
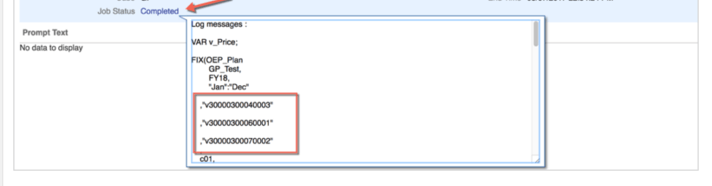
First, there is limited functionality in the Data Form validation rules. In this case, the functionality is there, but has an issue with the precision of the data. Even though Input equals Initialized (or appears to), validation fails and shows a different background color. I have seen this before with decimals with large precision.
How Groovy Solves This
Groovy calculations have the ability to traverse through the cells of a Data Form. The 8 cells that can be impacted by the 3 overrides can be checked against their counterpart in subsequent columns (comparing the same account in the Input source to the Initialized source). This is for another discussion, but Groovy can actually create temp grids and pull data directly from Essbase that doesn’t exist in the grid, too.
To simplify this, the following only loops through the first column – Avg Price / Case. This can be replicated easily for all subsequent columns by changing the account in question.
This example uses several Groovy methods/functions. First, the data grid is stored in a variable, as it will be referenced throughout. Next, we are using the dataCellIterator, which is the same in the previous post on Groovy. If you didn’t read that, or don’t understand the iterator, check that out.
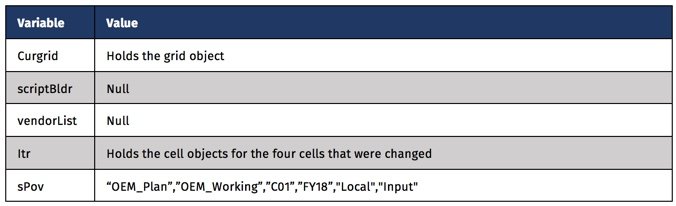
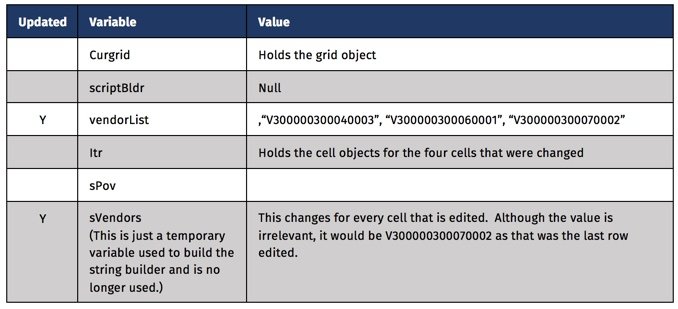
At this point, the calculation is requesting to loop through all the cells with Avg Price/Case AND Input in the POV. Inside the loop, lDestMembers is set to a list equal to all the members in the POV for the relative cell. memberNames returns every member in the POV in a Groovy list.
The next step is getting the value for the corresponding cell in the Initialized source. getCellWithMembers accomplishes this with the appropriate parameters passed. This function accepts member names, so all the members in the Input cell’s POV are used, excluding the source dimension. This is changed to Initialize.
Lastly, the comparison is made between the two cells. If they are not identical, setBgColor is executed on the Input source cell to identify it as something that has changed due to an override.
The Calculation
// Initialize a grid
DataGrid curDataGrid = operation.grid
// Set the color to be used if the values are not identical
def iColor = 16746496
// Loop through the cells in column that has
// Average Price/Case and Input in the POV
operation.grid.dataCellIterator('Avg_Price/Case','Input').each
{
// Get the POV for the cell
def lDestMembers = it.memberNames
// get the value in the Initialized source that is equivalent to
// the cell in the Input Source. The POV form the Input source
// is used with the exception of the source is changed to Initialize
def dValue = operation.grid.getCellWithMembers(lDestMembers[0].toString(),
lDestMembers[1].toString(),lDestMembers[2].toString(),
lDestMembers.toString(),lDestMembers[4].toString(),
lDestMembers[5].toString(),"Initialize",lDestMembers[7].toString(),
lDestMembers[8].toString(),lDestMembers[9].toString(),
lDestMembers[10].toString()).data
// if the value is different between the Input and Initialized source,
// change the background color
if(it.data != dValue)
{
it.setBgColor(iColor)
}
}
Data Form Changes
This new Groovy Business Rule should be added to the form and executed on load and save. This will ensure that the accounts that have been changed are identified both before, and after, the user makes any changes. One more note that might save you hours of frustration – make sure this rule runs last when other rules are also executed!
Conclusion
This opens up a lot of options that far surpass the default form validations. Other options are available.
- Tool-tips can also be assigned to a cell instructing the user how to resolve a validation error, if one exists.
- The form save can be interrupted, stopping the user from saving data on a form (or even saving only parts of the form) when validation errors exist.
- Data can be altered to force validation prior to saving.
- Detailed messages can be displayed with instructions and other communication to the user.
- Have specific calculations executed based on the data entered.
This is not an exhaustive list. We, as developers and architects, literally can do anything we want and have complete control over what happens and what doesn’t happen. This is exciting because we have nearly complete control over what happens on save. If you have other ideas, or questions, please share them with comments.